 Introduction:
Introduction:
Most motorists have at some stage seen spark plugs in vehicles – but apart from the obvious “spark”, they need to provide few are aware of exactly how it works and why it is important for safety on the road.
Spark plugs have a central role in the car functioning as the car depends on them for starting and running. The car spark plugs ignite the engine's gas mixture, providing the car with power and maintaining it functioning. They are an important part of the ignition and engine system and it is important that they are always in good shape.
In this section we would like to look at the spark plugs a bit closer and, with the assistance of our Road Safety Partner AutoZone share some frequently asked questions about spark plugs and the answers thereto.
Definition:
A spark plug is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/air mixture by an electric spark while containing combustion pressure within the engine.
A spark plug has a metal threaded shell, electrically isolated from a central electrode by a porcelain insulator. The central electrode, which may contain a resistor, is connected by a heavily insulated wire to the output terminal of an ignition coil or magneto. The spark plug's metal shell is screwed into the engine's cylinder head and thus electrically grounded. The central electrode protrudes through the porcelain insulator into the combustion chamber, forming one or more spark gaps between the inner end of the central electrode and usually one or more protuberances or structures attached to the inner end of the threaded shell and designated the "side", "earth", or "ground" electrode(s). [Wikipedia]
Which Spark Plugs do I need and when do I replace them?
Different driving conditions resulting in different temperatures in the combustion chamber will require spark plugs of different heat ranges. Fortunately, a spark plug that meets most driving conditions for the average passenger vehicle has already been identified by the manufacturer of your vehicle.
The car owner's manual provides important information on when to check each car part. This may also give an indication of when to replace spark plugs.
If the ignition or any other car areas related to the spark plugs functioning is not working properly then you should check them as well. If you are wishing to replace them yourself, you should make sure you know how and have not only the proper knowledge for it but also the right tools. You should avoid trying to replace the car spark plugs unless you are sure you know how to do it.
The car spark plugs can be replaced easily and in a few moments by someone who knows how to do it. In new cars, the spark plugs are usually controlled by the car computer and this allows checking them and tuning them much more easily than in older cars.
It remains good advice to check spark plugs after the 10.000 kilometres or around such date since they can stop functioning at any time since then. They may last much longer but it is best to avoid any nasty surprises on the road by checking them regularly.
What does a spark plug do?
It serves as a lighter to ignite the air/fuel mixture under extreme conditions. A spark plug must dissipate the heat produced by the combustion gases.
Voltage
It withstands high voltages between 20 000 V - 30 000 V.
Temperature
It withstands repeated cycles between normal operating temperatures 400ºC to 800ºC and 2500ºC
Chemicals
It withstands chemical corrosion caused by fuel and combustion gases
Pressure
It withstands a pressure of 50kg/cm squared.
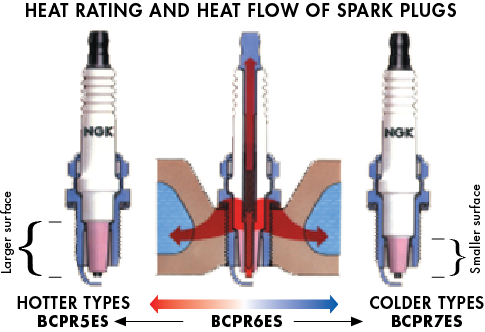
What do the numbers on the spark plug mean?
The numbers indicate the heat rating system. The heat rating is a measure of the amount of heat dissipation. Selecting a spark plug with the proper heat range will ensure that the tip will maintain a temperature high enough to prevent fouling yet be cool enough to prevent pre-ignition.
Hot types for low speeds
- It has a large surface exposed to the combustion gases.
- It dissipates heat slowly.
- The firing end heats up quickly.
Cold types for high speeds
- It has a smaller surface exposed to the combustion gases.
- It dissipates heat quickly
- The firing end does not heat up quickly.
Memo
It is essential to use a spark plug that fits a specific engine and its conditions of use.
When the heat rating is too high:
The spark plug temperature remains too low and causes deposit buildup on the firing end; the deposits provide an electrical leakage path that gives rise to loss of sparks.
When the heat rating is too low:
The spark plug temperature rises too high and induces abnormal combustion (pre-ignition); this leads to melting of the spark plug electrodes as well as piston seizure and erosion.
What does the 'R' stand for?
Resistor. The spark plug incorporates a ceramic resistor of 5K ohms to suppress ignition noise generated during sparking.

Features
- It removes noises which may interfere with car radios, mobile communications and cellular phones.
- It also prevents the incorrect operation of electronic fuel injection control systems.
Memo
As the resistor spark plug has an incorporated resistor, some people think that it has adverse effects on the start-up, acceleration, fuel economy and emissions. However, this is wrong. It does not affect engine performance so don’t hesitate to use it.
Why does my spark plug leak?
It does not leak. The stain on the ceramic is caused by the oil particles suspended in the air that adheres to the surface of the insulator due to the high voltage. It does not affect the spark plug’s performance in any way.

What makes up a spark plug?

How does one fit a spark plug?
Use the specified tightening torque applied to the spark plug.
Flat seat spark plugs with a thread diameter of 18, 14, 12 and 10mm
- New plugs 1/2 - 3/4 turn (180° - 270°)
- Re-used 1/12 - 1/8 turn (30° - 45°)
Spark plugs with a thread diameter of 8mm
- New plugs 1/3 turn (120°)
- Re-used 1/12 turn (30°)
| Thread Diameter |
Tightening Torque |
| 18 mm |
3.5 - 4.0 kgm |
| 14 mm |
2.5 - 3.0 kgm |
| 12 mm |
1.5 - 2.0 kgm |
| 10 mm |
1.0 - 1.2 kgm |
| 8 mm |
0.8 - 1.0 kgm |
How do you read a used spark plug?
Different manufacturers have specified service intervals for their vehicle’s spark plugs.
Examples of problems caused by excessively long periods of use:
- Worn out electrodes will have difficulty in sparking.
- Deposits accumulated on the firing end may induce abnormal combustion (pre-ignition), causing problems that include melting of the electrodes

Also View:
Vehicle maintenance and safety guide to roadworthiness of vehicles
Safety and Roadworthiness of Vehicles in Long-Term Parking or Lockdown
Vehicle Maintenance and Repair
Installing Spark Plug